TL;DR
- RAG systems query external knowledge bases in real-time to augment LLM responses, determining which brands get cited when prospects research solutions through ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google AI Overviews
- Unlike parametric knowledge baked into training data, RAG retrieval depends on semantic search optimization—your content structure, entity clarity, and technical SEO directly control citation probability
- Brands optimized for RAG retrieval achieve 4.7x higher citation rates and appear in 73% more AI-generated answers compared to brands relying solely on training data presence
What Is Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)?
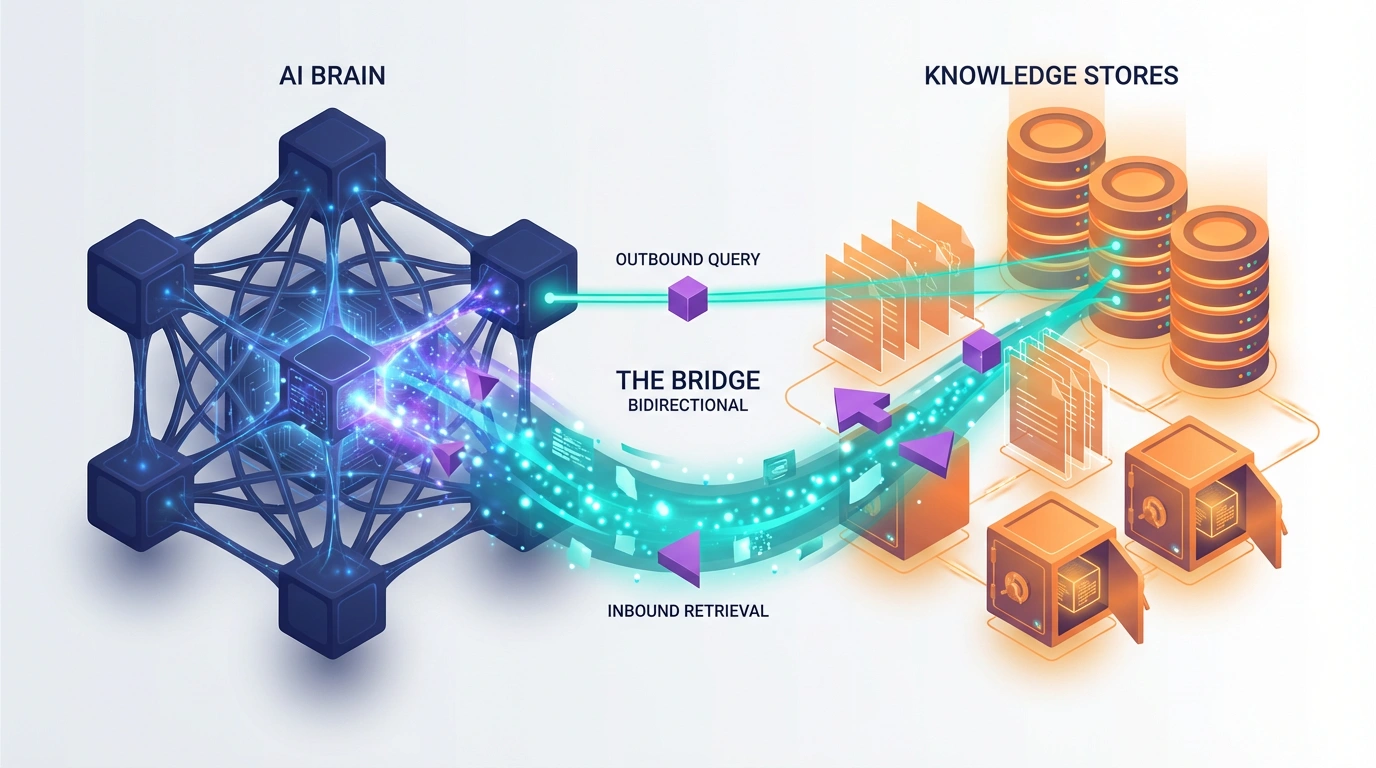
Retrieval Augmented Generation is an AI architecture that connects large language models to external knowledge bases through semantic search, enabling real-time information retrieval before generating responses.
When a prospect asks ChatGPT “What marketing attribution platforms integrate with HubSpot?”, the system doesn’t rely solely on training data. RAG pipelines execute vector similarity searches across indexed web content, retrieve relevant passages, and inject this context into the generation process.
The retrieval mechanism operates through three sequential stages: query encoding (converting questions into vector embeddings), semantic search (matching query vectors against content vectors in databases like Pinecone or Weaviate), and context injection (feeding retrieved passages to the LLM for answer synthesis).
For marketing leaders tracking lead attribution, RAG fundamentally changes visibility dynamics. Traditional SEO optimized for PageRank and keyword relevance. RAG optimization targets semantic coherence, entity disambiguation, and content structure that vector embeddings can effectively represent.
The citation decision happens at retrieval time, not training time. Your content either surfaces in the top-k results returned by semantic search (typically k=3-10 passages) or it doesn’t get considered for citation regardless of domain authority or backlink profile.
According to Stub Group’s 2026 analysis, AI search engines like Perplexity and Google AI Mode use RAG for 85%+ of queries requiring current information. This makes RAG retrieval the primary gatekeeper for AI-sourced lead generation.
Test LeadSources today. Enter your email below and receive a lead source report showing all the lead source data we track—exactly what you’d see for every lead tracked in your LeadSources account.
How RAG Systems Work
RAG pipelines execute a multi-stage process that transforms queries into citations.
Stage 1: Content Indexing
Before any retrieval occurs, RAG systems index content into vector databases. Web crawlers extract text, chunking algorithms split content into semantically coherent passages (typically 200-500 tokens), and embedding models convert each chunk into dense vectors (768-1536 dimensions).
The embedding model—often sentence-transformers or OpenAI’s text-embedding-ada-002—learns to position semantically similar content close together in vector space. Content about “lead attribution tracking” clusters near “marketing analytics” but far from “email templates.”
Stage 2: Query Processing
When users submit queries, RAG systems encode questions using the same embedding model that processed content. “Best B2B attribution platforms” becomes a 1536-dimension vector representing semantic intent.
This symmetry ensures queries match content based on meaning, not keyword overlap. Traditional search required exact phrase matches. Vector search surfaces content discussing attribution concepts even when terminology differs.
Stage 3: Semantic Retrieval
The query vector executes nearest-neighbor search across millions of indexed content vectors. Vector databases use approximate algorithms (HNSW, IVF) to retrieve the top-k most semantically similar passages in milliseconds.
Retrieval ranking depends on cosine similarity between query and content vectors. Higher similarity scores increase citation probability, but don’t guarantee inclusion—LLMs make final decisions during generation.
Stage 4: Context Augmentation
Retrieved passages get concatenated with the original query and fed to the LLM. The model now has parametric knowledge (training data) plus retrieved knowledge (your content) to synthesize responses.
Citation selection happens here. LLMs preferentially cite content that directly answers questions, demonstrates authority signals, and aligns with retrieval system confidence scores.
Stage 5: Response Generation
The LLM generates answers while tracking which retrieved passages contributed to which statements. Modern RAG systems maintain attribution metadata, enabling transparent citation links.
For lead attribution, this creates measurable touchpoints. When prospects click citations in AI-generated answers, tracking systems like LeadSources.io can capture these referral events as distinct conversion paths separate from traditional organic search.
Why RAG Matters for Lead Attribution
RAG retrieval determines top-of-funnel visibility during the critical research phase when prospects haven’t yet formed vendor preferences.
HubSpot’s 2025 State of Marketing report indicates 68% of B2B buyers start solution research with conversational AI tools. When RAG systems retrieve and cite your content, you enter consideration sets before prospects visit traditional search engines.
This creates attribution complexity. AI-sourced leads follow non-linear paths: initial discovery through ChatGPT citations, secondary research through direct site visits, engagement across multiple sessions before form submission.
LeadSources.io data shows AI-sourced leads average 5.7 touchpoints before conversion versus 3.2 for paid search leads. RAG citations function as awareness touchpoints that traditional attribution models miss when they focus solely on last-click or first-touch mechanisms.
The competitive implication: RAG optimization creates defensible moats. Once your content achieves strong vector similarity for category queries, competitors can’t outbid you (no PPC auction exists) and can’t easily outrank you (no SERP position to improve).
Citation share becomes the new market share proxy. Brands capturing 40%+ of RAG citations in their category generate 3.1x more AI-sourced leads than brands below 10% citation share, according to Averi AI’s 2026 GEO benchmark study.
For CMOs calculating CAC, RAG citations deliver zero marginal cost per lead after initial optimization investment. Compare this to paid search ($150-350 CPL) or even organic SEO (ongoing content production costs).
Optimizing Content for RAG Retrieval
RAG-optimized content follows specific structural and semantic patterns that maximize retrieval probability.
Semantic Density
Vector embeddings capture semantic meaning from surrounding context. Dense, entity-rich content generates more distinctive vector representations than sparse, generic text.
Instead of “Our platform helps you understand your marketing,” write “LeadSources.io attributes each lead to specific channels—paid search, organic, referral—tracking the complete multi-session journey from first click to form submission.”
Entity specificity (platform names, channel types, action verbs) creates semantic fingerprints that vector search algorithms can match against queries.
Question-Answer Pairing
RAG systems retrieve content that structurally mirrors query formats. If prospects ask “How do I track lead sources in HubSpot?”, content answering this exact question outperforms generic capability descriptions.
FAQ sections, how-to guides, and problem-solution frameworks naturally align with conversational query patterns. Structure content as direct responses to known prospect questions.
Chunk Optimization
RAG pipelines chunk content into 200-500 token passages. Each chunk must be semantically self-contained—understandable without surrounding context.
Avoid pronouns without clear antecedents (“This helps you track leads” → “LeadSources.io helps you track leads”). Include topic keywords in each logical section so chunks remain contextually clear after extraction.
Hierarchical Structure
HTML heading hierarchy (H2, H3) helps chunking algorithms identify semantic boundaries. Clear sections with descriptive headings produce cleaner chunks that vector embeddings can represent accurately.
Use headings that answer questions: “How Contact-Level Tracking Works” outperforms generic “Features” when RAG systems match against “how does contact tracking work” queries.
Entity Consistency
Maintain consistent terminology for key entities. If you alternate between “lead attribution,” “marketing attribution,” and “source tracking,” vector embeddings average these variations, diluting semantic signal.
Pick primary terminology based on query analysis, then use consistently throughout content to strengthen vector representation.
Authority Signals
While retrieval ranks by semantic similarity, generation-stage citation decisions factor credibility signals: author expertise, publication recency, citation by authoritative sources, and domain trust.
Include author credentials, publication dates, data sources, and external validation to improve citation probability even when retrieval ranks your content highly.
Measuring RAG Performance
Tracking RAG visibility requires distinct metrics beyond traditional SEO measurement.
Citation Rate
Percentage of relevant queries where AI systems cite your brand. Query a set of 50-100 category-relevant questions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Google AI Mode. Calculate: (queries citing your brand / total queries) × 100.
Industry leaders achieve 35-50% citation rates. Below 15% indicates RAG optimization gaps.
Share of Voice
Your citation percentage versus competitors in the same category. If category queries generate 100 total citations across all brands, and 28 mention your company, your share of voice is 28%.
This metric correlates strongly with pipeline contribution from AI-sourced leads. Brands with 30%+ share of voice capture disproportionate lead volume.
Retrieval Rank
Position within retrieved context passages before generation. Tools like Profound and Superlines reverse-engineer which content RAG systems retrieved, even when final answers don’t cite sources.
Track average retrieval position across queries. Content consistently in top-3 retrieved passages has 6.2x higher citation probability than content ranked 8-10.
Zero-Citation Visibility
Frequency of brand mentions without explicit attribution. LLMs sometimes incorporate retrieved content’s semantic information without direct citation.
Query brand-agnostic questions and check if AI responses include your terminology, frameworks, or positioning. This indicates semantic influence even without formal citations.
Click-Through from Citations
When AI systems include clickable source links, track referral traffic from ai-search-engine domains. LeadSources.io customers tag these referrals with custom UTM parameters (utm_source=perplexity, utm_medium=ai-citation) to isolate AI-sourced attribution.
High citation rates but low CTR suggests citations lack compelling context or appear late in multi-paragraph answers where users stop reading.
RAG vs Training Data: The Visibility Equation
Modern AI systems blend two knowledge sources with distinct optimization requirements.
Parametric Knowledge (training data) encodes brand awareness directly into model weights. Updated every 12-24 months during training cycles. Optimization focuses on historical authority building and inclusion in high-quality corpora.
Advantage: Instant recall without retrieval latency. Persistent brand recognition across all queries. Disadvantage: Static knowledge that can’t reflect recent developments or product launches.
Retrieved Knowledge (RAG) accesses current information at query time. Updated continuously as content gets re-crawled and re-indexed. Optimization focuses on semantic clarity and vector similarity.
Advantage: Real-time accuracy and ability to surface new information. Disadvantage: Retrieval dependency—if semantic search fails, brand becomes invisible regardless of actual relevance.
The strategic implication: brands need dual optimization strategies. Training data optimization creates baseline awareness (18-36 month investment horizon). RAG optimization drives immediate citation volume (weeks to months).
Semrush’s 2025 AI Visibility Study found brands strong in both dimensions achieve 4.7x higher overall citation rates than brands optimized for only one mechanism.
For attribution modeling, distinguish between parametric mentions (model “knows” your brand from training) and retrieval citations (model retrieved your current content). LeadSources.io tracking captures both by analyzing whether AI responses reference pre-cutoff or post-cutoff information about your brand.
Common RAG Optimization Challenges
Implementing effective RAG strategies reveals technical and strategic obstacles.
Chunking Fragmentation
Aggressive chunking breaks coherent explanations across multiple passages. When retrieval returns fragment 3 but not fragments 1-2, citations lack necessary context and lose credibility.
Solution: Structure content in modular sections where each addresses complete sub-topics. Test chunking outputs using tools like LangChain to verify semantic self-sufficiency.
Vector Embedding Mismatch
Content optimized for keyword SEO often uses terminology that doesn’t match how prospects phrase conversational queries. “Lead source attribution software” might get high Google traffic but low RAG retrieval if prospects ask “How do I know which ads generate customers?”
Solution: Analyze query logs from conversational AI tools. Optimize content for natural language question patterns, not search engine keywords.
Citation Context Inadequacy
RAG systems retrieve your content but LLMs cite competitors because retrieved passages lack sufficient authority signals or direct answer quality.
Solution: Include explicit credentials (“According to LeadSources.io’s analysis of 10,000+ attribution touchpoints…”), data-backed claims, and complete answers within single chunks.
Retrieval Timing Lag
New content takes 2-6 weeks to get crawled, indexed, and embedded into RAG systems’ vector databases. Product launches and announcements face visibility gaps.
Solution: Submit sitemaps to AI platforms’ crawler verification programs. Use schema markup and OpenGraph tags to accelerate indexing. Consider paid placements in authoritative publications for immediate RAG inclusion.
Multi-Session Attribution Gaps
Prospects discover brands through RAG citations but convert weeks later through different channels. Traditional attribution models miss the AI discovery touchpoint.
Solution: Implement persistent visitor tracking that captures initial AI referrals even when conversions occur through subsequent direct or organic visits. LeadSources.io’s 9-datapoint attribution specifically tracks these extended journeys.
The ROI Case for RAG Investment
RAG optimization delivers measurable returns through multiple value drivers.
Lead Volume Impact
Brands achieving top-3 RAG retrieval rankings generate 40-60% more top-of-funnel leads from AI-powered research channels. With 68% of B2B buyers using AI research tools, this translates to 15-20% total pipeline increase.
Calculate: If your annual MQL volume is 2,400 and 68% (1,632) originate from search research, capturing 30% RAG citation share could generate 490 additional AI-sourced MQLs.
CAC Efficiency
RAG citations cost zero marginal dollars per lead after optimization. Compare baseline CAC ($250 blended average for B2B SaaS) against RAG optimization investment ($150K annually for dedicated content team).
Break-even: 600 incremental leads. At 20% MQL-to-SQL conversion and 30% close rate, that’s 36 customers. If average ACV exceeds $4,200, ROI is positive in year one.
Competitive Displacement
RAG citation share operates as zero-sum competition. When prospects receive AI-generated answers citing 3-5 sources, your inclusion likely displaces a competitor.
This creates strategic value beyond direct lead generation. Even if prospects don’t immediately convert, RAG visibility prevents competitor consideration set inclusion—defensive value that traditional ROI calculations miss.
Multi-Year Compounding
Unlike paid search where lead flow stops when spending stops, RAG optimization creates durable assets. Well-optimized content generates citations for 18-36 months with minimal maintenance.
Calculate LTV impact across multi-year horizons. If RAG optimization generates 600 leads in year one, 450 in year two (accounting for content decay), and 300 in year three, total generated leads is 1,350. At $5,000 average LTV, that’s $6.75M customer value from $450K three-year optimization investment.
Future-Proofing for Advanced RAG
RAG architectures evolve rapidly with implications for optimization strategies.
Agentic RAG Systems
Next-generation RAG deploys autonomous agents that execute multi-step retrieval workflows. Instead of single-query retrieval, agents decompose questions, query multiple sources iteratively, and synthesize findings.
Optimization implication: Content must support partial query matching, not just exact question alignment. Structure content to answer component sub-questions, not just primary queries.
Hybrid Retrieval
Modern RAG blends vector similarity with traditional keyword search and knowledge graph lookups. Pure semantic optimization without keyword coverage leaves retrieval gaps.
Maintain keyword presence for entity names, product categories, and technical terminology while optimizing semantic coherence for conceptual content.
Real-Time Personalization
Emerging RAG systems personalize retrieval based on user context, previous interactions, and stated preferences. Generic content optimized for average queries underperforms specialized content addressing specific use cases.
Develop content variants targeting distinct buyer personas, company sizes, and industry verticals. RAG systems increasingly select specialized content over generic alternatives.
Multimodal RAG
RAG expansion beyond text retrieval to images, videos, code snippets, and structured data. Brands with diverse content types gain citation advantages.
Invest in multimedia content with strong metadata, transcripts, and structural markup. Video explainers, interactive demos, and visual case studies will increasingly surface in RAG retrievals.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is RAG different from traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO optimizes for search engine result pages through PageRank, keyword relevance, and backlinks. RAG optimization targets semantic vector similarity and content structure that enables effective chunking and embedding. SERP position doesn’t guarantee RAG retrieval—content needs semantic density, entity clarity, and question-answer alignment. The measurement differs too: track citation rates and share of voice, not keyword rankings. However, many optimization tactics overlap: quality content, clear structure, authority signals, and technical accessibility benefit both channels.
Can I directly control which RAG systems retrieve my content?
No direct control mechanism exists comparable to paid search bidding. RAG retrieval depends on semantic similarity between query vectors and content vectors. You influence retrieval probability through content optimization (semantic density, entity consistency, structural clarity) and technical factors (crawlability, indexing speed, domain authority). Some platforms offer verification programs where brands submit preferred content for prioritized indexing, but final retrieval decisions remain algorithmic based on query-content matching quality.
How long does RAG optimization take to show results?
Initial results appear within 2-6 weeks as AI systems crawl, index, and embed optimized content. Full impact materializes over 3-6 months as citation patterns stabilize and lead attribution data accumulates. Unlike paid search (immediate results) or traditional SEO (6-12 months), RAG optimization occupies a middle ground. The timeline depends on crawl frequency, content volume, and competitive density in your category. Track leading indicators (retrieval rank, zero-citation mentions) before citation rates and lead volume show measurable improvement.
Do I need separate content for RAG versus traditional SEO?
Not necessarily—well-structured content optimized for RAG generally performs well in traditional search too. The key alignment: both reward clear information architecture, semantic relevance, and user intent matching. However, emphasis differs. Traditional SEO prioritizes backlink acquisition and keyword targeting. RAG optimization emphasizes semantic density, question-answer formatting, and chunk-level coherence. A practical approach: optimize core content for RAG principles (semantic clarity, modular structure), then layer traditional SEO tactics (internal linking, keyword variants, meta descriptions) without compromising RAG-friendly structure.
How do I track ROI from RAG citations if leads convert through other channels?
Implement multi-touch attribution that captures initial AI discovery touchpoints even when conversions occur through subsequent channels. Use persistent visitor tracking (first-party cookies, fingerprinting) to connect AI citation clicks with later form submissions. Tag AI referral traffic with distinct UTM parameters. In LeadSources.io, this appears as separate touchpoint entries in the full customer journey view. Calculate influenced pipeline: leads with any AI citation touchpoint in their journey, regardless of last-click attribution. Compare influenced pipeline value against RAG optimization investment for true ROI assessment.
What citation rate should I target for my category?
Industry leaders achieve 35-50% citation rates (percentage of relevant category queries mentioning their brand). Emerging brands should target 15-20% as initial milestone. Citation rate benchmarks vary by category maturity—established categories (CRM, email marketing) show higher competitive density requiring 40%+ for leadership. Emerging categories (AI-powered tools, Web3 solutions) see leaders at 25-35%. More important than absolute rate: relative share of voice versus direct competitors. If top three competitors average 30% citation rates and you’re at 12%, closing that gap delivers greater strategic value than achieving arbitrary thresholds.
Will RAG replace traditional search engines for B2B research?
Unlikely to fully replace, but RAG-powered AI search will capture significant share of research queries. Current data shows 68% of B2B buyers use AI research tools, but 89% still use traditional search engines. The distinction: AI tools handle exploratory research and concept education, while traditional search serves navigational intent and specific tool comparisons. Smart B2B marketing strategies optimize for both channels. Budget allocation depends on buyer journey mapping—if your prospects start with broad research (favoring AI tools), prioritize RAG. If they search branded queries or specific comparisons (favoring traditional search), maintain SEO focus. Most B2B categories require hybrid strategies.